Learning Process
This page covers Task B. Learning Process from the FAA-S-ACS-25 Flight Instructor for Airplane Category Airman Certification Standards.
Definitions of Learning
Learning
The change in behavior that results from experience and practice.
Learning Theory
- Primary learning theories
- Classical conditioning - Pavlov's dog
- Operant conditioning - a positive behavior creates a positive consequence; a negative behavior creates a negative consequence. The learner then makes an association between behaviors and consequences and then predicts that future behaviors will result in similar consequences.
- Social learning - Social learning is simply learning by observation
- Modern learning theories grew out of two concepts of how people learn: behaviorism and cognitive theory.
Behaviorism
- Explains behavior entirely in terms of observable and measurable responses to stimuli and is not really used for education.
Cognitive theory
- Focuses on what is going on inside the mind.
- It is more concerned with cognition (the process of thinking and learning)-knowing, perceiving, problem-solving, decision-making, awareness, and related intellectual activities-than with stimulus and response
- Learners progress from simple to complex
- Use SBT
Perceptions and Insight
- Perception
- To give meaning to sensations and is the basis of all learning
- Learning occurs most rapidly when using more than one sense
- Several factors affect a learners ability to perceive (G-STEP) - to perceive well need to
- Goals and Values
- Aligned with learner's goals
- Self-concept
- Be confident
- A learner's self-image (e.g. confidence or insecurity) has a strong effect on perception
- Time and Opportunity
- Be given time to adequately perceive
- Element of Threat
- Not feel threatened
- Physical Organism
- Actually be able to hear/see etc.
- Goals and Values
- Insight
- Involves the grouping of affiliated perceptions into meaningful wholes
- Creating insight is one of the instructor's major responsibilities
- Forgetting is less of a problem when there are more anchor points for tying insights together.
- It is a major responsibility of the instructor to organize demonstrations and explanations, and to direct practice so that the learner has better opportunities to understand the interrelationship of the many kinds of experiences that have been perceived.
- Insights involve
- Learner's ability to remain receptive to new experiences
- Helping the student acquire and maintain a favorable self-concept
- Provide a secure and nonthreatening, safe environment in which to learn
Acquiring knowledge
Mental Model
Refers to an organized collection of ideas that forms a learner's understanding of a thing or process, and evolve as new information is learned.
- CFI job is helping learners acquire knowledge
- Memorization
- Can help learner get started quick (e.g. memorize how to set altimeter setting) but doesn't generalize to new situations
- Understanding
- Understanding develops when learners begin to organize known facts and steps into coherent groups that come together to form an understanding of how a thing or a process works.
- Concept Learning
- By grouping information into concepts, humans reduce the complexities of life and create manageable categories
Laws of Learning
- The laws of learning (REEPIR)
- Readiness
- The basic needs of the learner need to be satisfied before he or she is ready or capable of learning
- Learners make more progress if they have a clear objective
- Effect
- Behaviors that lead to satisfying outcomes are likely to be repeated
- Based on the emotional reaction of the learner
- Exercise
- Practice / "use it or lose it"
- Primacy
- What is learned first is most sticky
- Creates strong unshakable impression
- Important to teach things right the first time
- Intensity
- More vivid learning experience more likely to be remembered
- Recency
- What is learned most recently is also sticky
- Often determines the sequence of lectures within a course of instruction
- Readiness
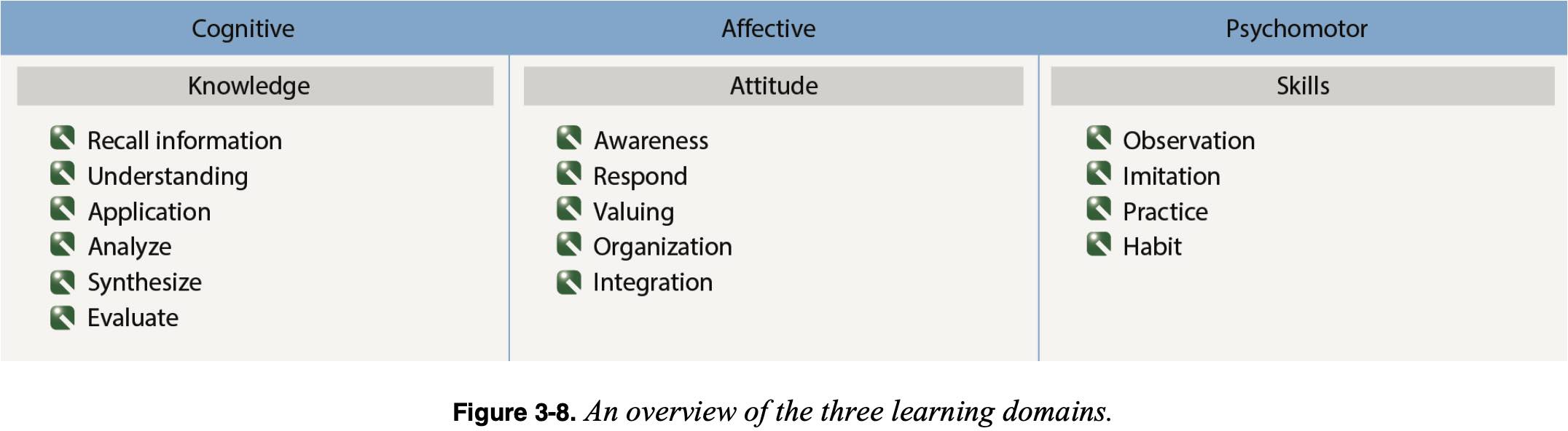
Domains of Learning
- Domains of learning (CAP)
- Cognitive (thinking)
- Affective (feeling)
- Psychomotor (doing)
- Below also has
- Heirarchy or taxonomy for each from most to least complex top to bottom
- Educational levels of objectives or goals of each level or what you are looking for in your learner
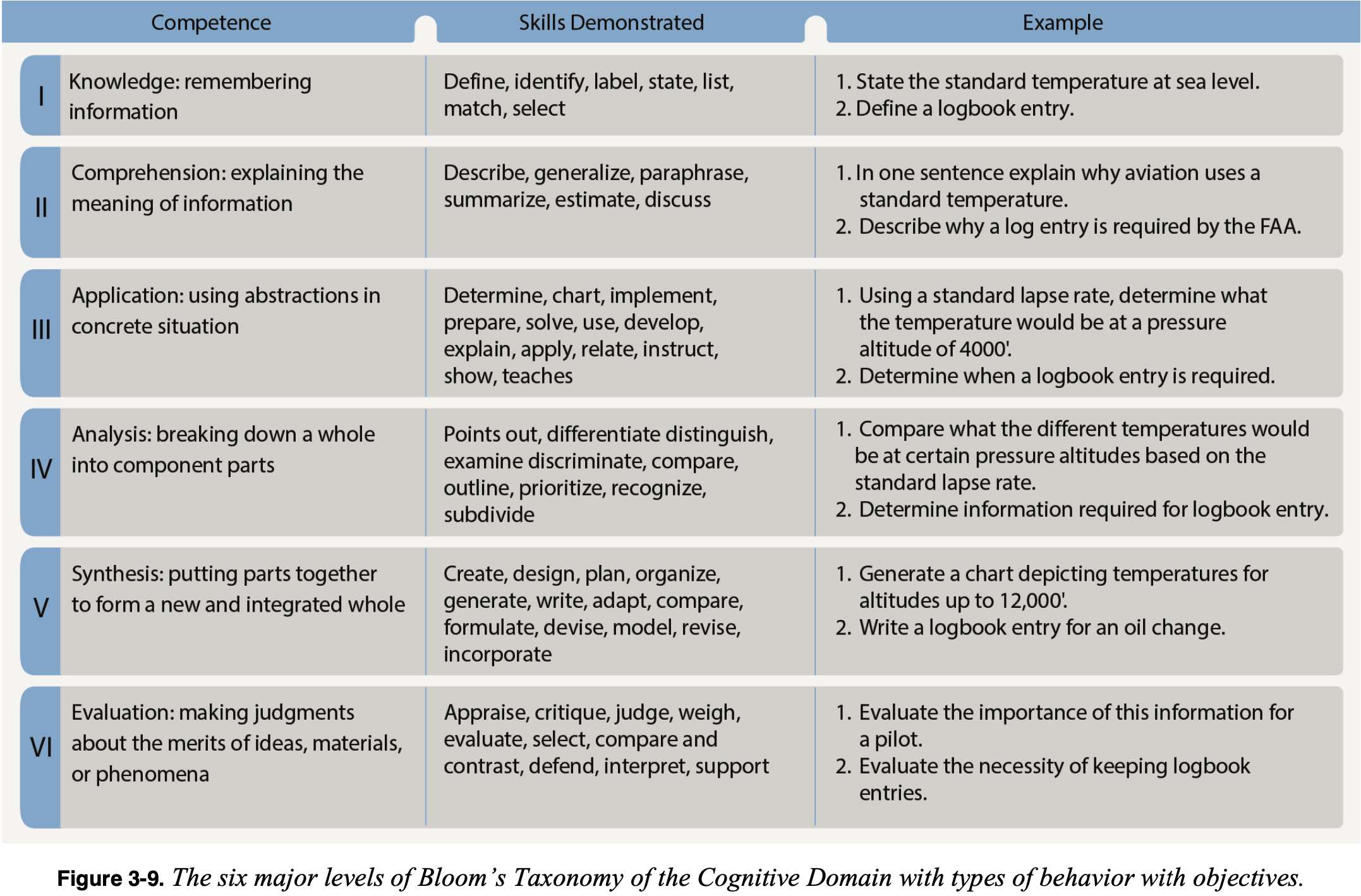
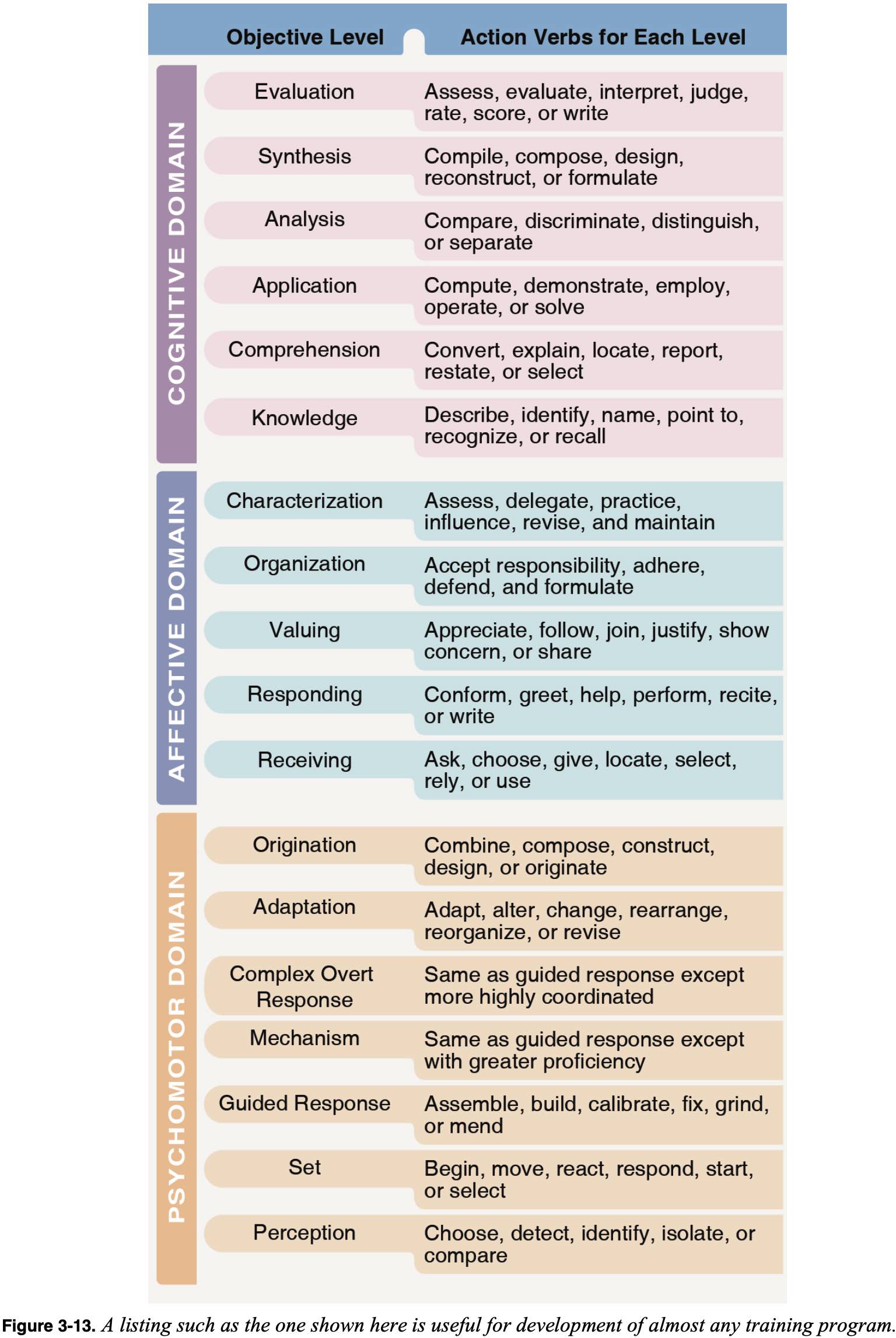
Cognitive
- Remembering specific facts and concepts
- Acquiring knowledge like watching the King Schools video
- Taxonomy (most complex to least below)
- Evaluation - can use judgement to evaluate
- Synthesis - can create brand new relationships and see how they relate to each other
- Analysis - can see relationships
- Application - can go from specific to general
- Comprehension - can interpret what you've learned and extrapolate to the whole situation
- Knowledge - can recall or recognize something
- Cognitive educational levels of objectives
- Evaluation
- Analysis
- Application
- Comprehension
- Recall
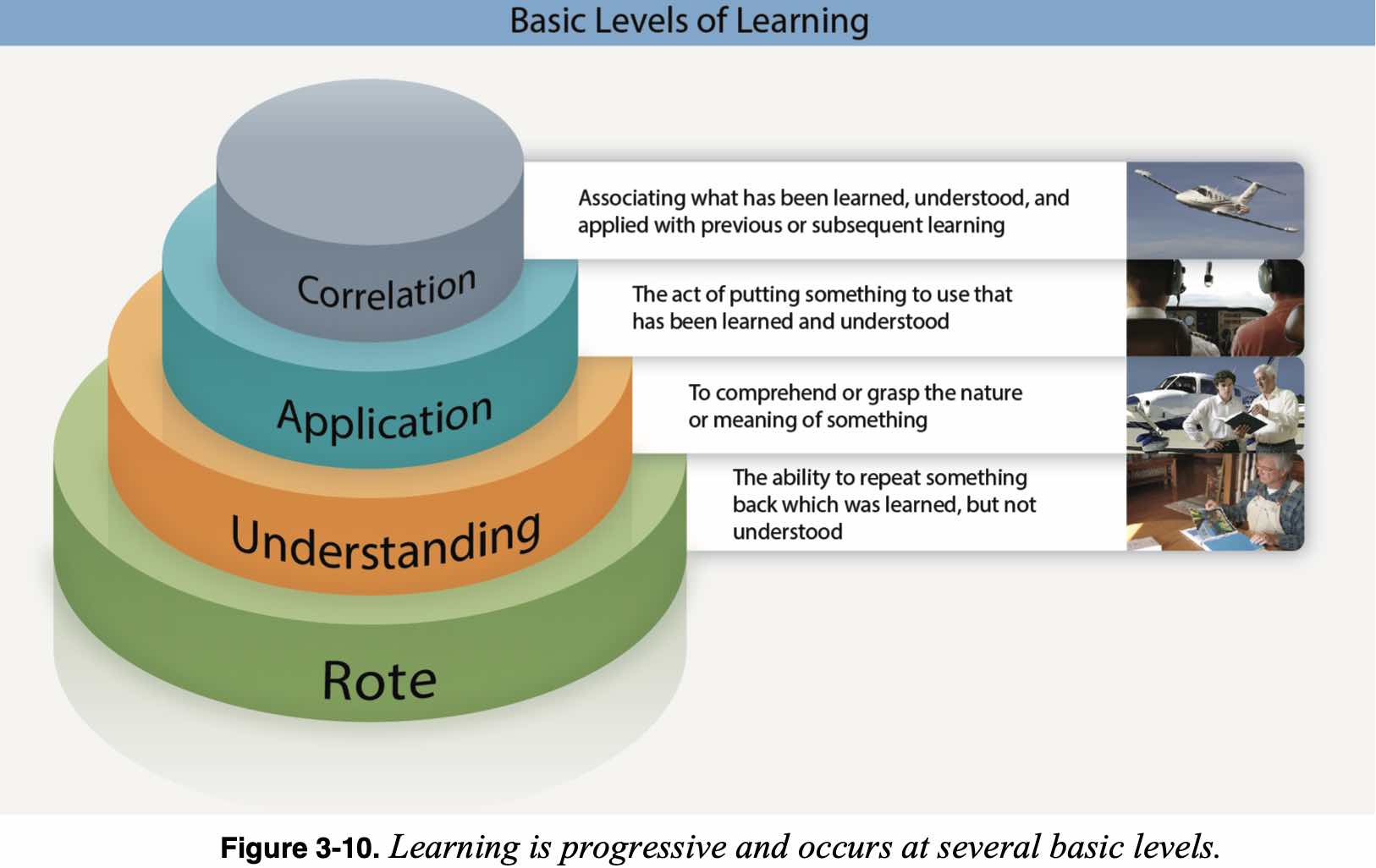
Levels of Learning
- Levels of Learning (RUAC)
- Rote
- Pure memorization - can parrot things back
- e.g. recalling stalling speed of an aircraft
- Understanding
- Ability to notice similarities and make associations between the facts and procedural steps learned
- e.g. how does stalling speed vary with loading
- Application
- Level where most instructors stop teaching
- e.g. learner can apply the knowledge during slow flight
- Correlation
- Associating previous learning with a new situation
- Rote
Affective
- Addresses a learner's emotions toward the educational experience - motivation and enthusiasm are important
- e.g. learning that is focused on developing attitude toward safety
- Taxonomy (most complex to least below)
- Characterization - when have incorporated the new value into your life and character
- Organization - when have rearranged your values to incorporate the new belief or value
- Valuing - have accepted into the learners value system and are complying
- Responding - information is changing behavior
- Receiving - willing to pay attention
- Affective educational levels of objectives
- Integration
- Organizing
- Value
- Response
- Awareness
Psychomotor
- Skill based and includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas
- Examples include learning to fly a precision instrument approach procedure, programming a GPS receiver, or using sophisticated maintenance equipment.??? Another question had flying a precision instrument approach procedure as cognitive domain...
- Taxonomy (most complex to least below)
- Origination - when you can try new ways of doing it on your own and develop new patterns and have creativity
- Adaptation - can modify for complex problems
- Complex Overt Response - can do skilled performance of complex task
- Mechanism - can perform simple tasks well
- Guided Response - can perform somewhat
- Set - relate those and know about them and they become cues
- Perception - having stimuli come in and affect your sense
- Psychomotor educational levels of objectives
- Habit
- Practice
- Imitation
- Observation
Characteristics of learning
- To be effective, the learning situation / characteristics of learning should be (PEMA)
- Purposeful
- Experience - based on
- Multifaceted
- Active Process - involve
- Some elements of learning (different types of learning) are (VCP PME) (page 3-19)
- Verbal
- Conceptual
- Perceptual
- Problem solving
- Motor
- Emotional
Scenario-Based Training
- Provides more realistic decision-making opportunities because it presents tasks in an operational environment
- Correlates new information with previous knowledge
- Introduces new information in a realistic context
- Uses a structured script of "real-world" scenarios
- Has the learner formulate possible solutions, evaluate the possible solutions, decide on a solution, judge the appropriateness of that decision and finally, reflect on the mental process used in solving the problem
- One of the primary methods to teach today's aviation learners how to make good aeronautical decisions
Acquiring Skill Knowledge
- See page 3-23
- An everyday example of skill knowledge is the ability to ride a bicycle.
Stages
- Three stages of skill aquisition (CAA)
- Cognitive stage
- Acquiring factual knowldge needed to perform the task
- Associative stage
- Putting it together combine individual steps and performance with likely outcomes
- Characterized by a learner who is able to assess personal progress and adjust performance accordingly
- Automatic response stage (Automaticity)
- Learner performs (e.g. landing) smoothly and without hesitation while simultaneously performing other tasks
- Takes deliberate practice that is aimed at a particular goal
- Cognitive stage
Knowledge of Results
- A learner may know that something is wrong, but not know how to correct it.
- Make certain that the learners are aware of their progress and let them know when they are right.
- They should be told as soon after the performance as possible, and should not be allowed to practice mistakes.
- Better to learn correctly in the first place than to learn wrong and then have to fix.
- One way to make learners aware of their progress is to repeat a demonstration or example and to show them the standards their performance should ultimately meet.
How to Develop Skills
- Power law of practice - progress depends on and gets better with repeated practice.
Learning Plateaus
Learning Plateau
A temporarily decreased or stalled rate of learning.
- Let learner know it's normal, only temporary, and not to get discouraged
- Move to another portion of the curriculum
- Most likely to occur pre-solo
- Pre-solo this can happen with making radio calls and/or landings
- Also be sure to set expectations ahead of time, and let them know that plateau at this stage is common, and then after solo the rest of private pilot training goes quickly
Types of Practice
- Three types of practice (DBR)
- Deliberate
- Practices specific areas for improvement and receives specific feedback after practice
- Better results are achieved if distractions are avoided during deliberate practice
- Necessary for a learner to learn to perform a skill on the automatic level
- Blocked
- Repeating the same drill or task until the movement becomes automatic?
- Random
- Deliberate
- Avoid deliberate feedback during deliberate practice
Evaluation versus Critique
- Page 3-28
- In the initial stages of skill acquisition, practical suggestions are more valuable to the learner than a grade.
- An instructor ensures a skill is practiced correctly by monitoring the practice and providing feedback about the skill development.
Distractions, Interruptions, Fixation, and Inattention
- Page 3-30
- A distraction is an unexpected event that causes the learner’s attention to be momentarily diverted.
- An interruption is an unexpected event for which the learner voluntarily suspends performance of one task in order to complete a different one.
- Fixation occurs when a learner becomes absorbed in performing one task to the exclusion of other tasks.
- Inattention occurs when a learner fails to pay attention to a task that is important.
Errors
- Page 3-33
- Slip
- A slip occurs when a person plans to do one thing, but then inadvertently does something else.
- Slips are errors of action.
- Mistake
- A mistake occurs when a person plans to do the wrong thing and is successful.
- Mistakes are errors of thought.
- Reducing errors
- The first line of defense against errors is learning and practice.
- Errors can often be reduced by working deliberately at a comfortable pace.
- Another way to help avoid errors is to look actively for evidence of them, and learners should learn to check their work.
Memory
- Multistage process with three systems (SrSL)
- Sensory register
- Short term, working memory
- Long term, storage memory
- Learning skills
- Task performance
- Clear step-by-step example (demonstration)
- Practice makes permanent (don't allow learner to practice mistakes)
- Learner performance planning
- Length of training session
Sensory register
- Takes in information from the environment (may be selected)
- Receives input from the environment and quickly processes it according to the individual's preconceived concept of what is important.
Short-Term and Long-Term
Short-Term
- Receives information from sensory register and stores for temporary use
- Has limit of about 7 chunks of memory
- Coding is using mnemonics and rhymes
- Has three basic operations: iconic memory, acoustic memory, and working memory
- Mnemonic
- Uses a pattern of letters, ideas, visual images, or associations to assist in remembering information
- Mnemonics include but are not limited to acronyms, acrostics, rhymes, and chaining.
- Recoding
- Taking new information and relating it existing knowledge and building new relationships
- Precoding
- A selective process where the sensory register is set to recognize certain stimuli and immediately transmit them to the short-term memory (STM) for action
- An example of sensory precoding is recognition of a fire alarm: no matter what is happening at the time, when the sensory register detects a fire alarm, the working memory is immediately made aware of the alarm and preset responses begin to take place.
- Why it's important to drill on emergency procedures
Long-Term
- Where information is stored for future use
- Activated by schemas, helps process new information
- Memory also applies to psychomotor skills, allowing for execution with very little thought.
- For example, it allows the ability to instinctively perform certain maneuvers or tasks, allowing more time to concentrate on other duties such as navigation, communications, and visual scanning for other aircraft.
Usage
- Page 3-37
- The ability to retrieve knowledge or skills from memory is primarily related to:
- Frequency of use
- Recency of use
Forgetting
- Page 3-37
- Forgetting (RID)
- Repression (Suppression)
- Interference (through overshadowing or displacement)
- Disuse (Fading)
Retention of learning
- Principles that have direct application to remembering / how to assist students in remembering what has been learned (PAFAR)
- Praise
- Response that gives a pleasurable return
- Stimulates remembering
- Association - recall by
- e.g. mnemonics
- Favorable attitudes
- Enjoy thinking about and remembering things that you like
- All senses used
- Learn with as many senses as possible
- Repetition
- 3 to 4 repetitions
- Praise
Transfer of learning
- When something learned in one place can be applied in another place
- Positive transfer
- If learning A helps learn B
- e.g. rectangular course helps traffic pattern
- Negative transfer
- If learning A hinders learning of B
- e.g. driving a car may make harder to steer rudders with feet
- Transfer of learning is promoted by the correlation level of learning
- Creating correct habits
- Building block technique
- One of the most basic and successful methods of teaching
- Ensures that the individual will learn proper habits and correct techniques
- Building block technique