Pilot Qualifications
This page covers Task A. Pilot Qualifications from the FAA-S-ACS-6C Private Pilot Airman Certification Standards.
Objective
To determine the applicant exhibits satisfactory knowledge, risk management, and skills associated with airman and medical certificates including privileges, limitations, currency, and operating as pilot-in-command as a private pilot.
Certification, Currency, and Recordkeeping Requirements
- There are several requirements to obtain various levels of pilot certificates described in 14 CFR Part 61
- Eligibility requirements
- e.g. age, knowledge test requirements, endorsements
- Aeronautical knowledge areas
- Flight proficiency
- Maneuvers the pilot should be able to perform
- Aeronautical experience
- The number of hourse spent on various flight training activities
- Eligibility requirements
- These are broken down by the level of pilot certificate below
- Also included in the below are the privileges and limitations of each level of pilot certificate
Student Pilot
Eligibility Requirements
- 14 CFR §61.83
- 16 years old
- Except 14 years old for glider or balloon
- Read, speak, write, and understand English
Aeronautical Experience
- No aeronautical experience required to be a student pilot
Privileges and Limitations
- 14 CFR §61.89
- A student pilot may not act as pilot in command of an aircraft
- That is carrying a passenger
- That is carrying property for compensation or hire
- For compensation or hire
- In furtherance of a business
- On an international flight
- Except that a student pilot may make solo training flights from Haines, Gustavus, or Juneau, Alaska, to White Horse, Yukon, Canada, and return over the province of British Columbia;
- With a flight or surface visibility of less than 3 statute miles during daylight hours or 5 statute miles at night
- When the flight cannot be made with visual reference to the surface
- In a manner contrary to any limitations placed in the pilot's logbook by an authorized instructor
- A student pilot may not act as a required pilot flight crewmember on any aircraft for which more than one pilot is required by the type certificate of the aircraft or regulations under which the flight is conducted, except when receiving flight training from an authorized instructor on board an airship, and no person other than a required flight crewmember is carried on the aircraft
- CFI endorses the student logbook for the specific make and model for the aircraft to be flown, good for 90 days.
- With proper documentations, as mentioned above, solo PIC flight can be completed to specific destinations or areas by the student pilot.
- Can use BasicMed
- Student pilots are required to carry their logbook on solo cross-country flights
Subparagraph (i) of 14 CFR §61.1(b) Cross-country time states the following
includes a landing at a point other than the point of departure
Subparagraph (ii) say that for the purposes of meeting aeronautical experience requirements for a private pilot certificate the cross-country flight must include a point of landing more than 50 nm from the point of departure
This seems to mean that student pilots must carry their logbook on any flight that involves a landing at a point other than the point of departure, even if such a flight cannot count towards aeronautical experience requirements for a private pilot certificate
It is probably best for student pilots to just get in the habit of keeping their logbook in their flight bag so it is always with them when they fly.
Notes
- Student pilot certificates never expire
- Have student pilot apply for student pilot certificate via IACRA right away
- Student pilot certificate is physical plastic card just like any other pilot certificate
Private Pilot
Eligibility
- 14 CFR §61.103
- 17 years old
- Except 16 years old for glider or balloon
- Read, speak, write, and understand English
- Receive training, endorsements, meet experience requirements, etc.
Aeronautical Experience
- 14 CFR §61.109
- 40 hours total flight time
- 20 hours flight training (on Private Pilot areas of operation in 14 CFR §61.107(b))
- 3 hours cross country
- 3 hours night
- One cross country flight of over 100 nm total distance
- 10 T/O's and 10 landings to a full stop with each involving a flight in the traffic pattern at an airport
- 3 hours by reference to instruments in a single engine airplane
- 3 hours in a single engine airplane within 2 calendar months prior to the practical test
- 10 hours solo flight (in a single engine airplane)
- 5 hours of solo cross country flying
- One solo cross country flight of at least 150 nm total distance with full stop landings at 3 points and one segment of at least 50 nm between T/O and landings
- 3 T/O's and landings to a full stop at an airport with an operating control tower
- 20 hours flight training (on Private Pilot areas of operation in 14 CFR §61.107(b))
Privileges and Limitations
- 14 CFR §61.113 - Private pilot privileges and limitations: Pilot in command
- 14 CFR §61.117 - Private pilot privileges and limitations: Second in command of aircraft requiring more than one pilot
- No person who holds a private certificate may act as a PIC of an aircraft carrying passengers or property for hire, or as PIC of an aircraft for hire/compensation.
- Only if the aircraft is in connection to any business and is only incidental to that business or employment, and the aircraft does not carry passengers of property for compensation or hire.
- Must pay at least their pro rata share of flight operating expenses
- A private pilot may act as the PIC for a charitable, nonprofit, or community event of a flight as described in 14 CFR §91.146, if the sponsor and pilot comply with 14 CFR §91.146.
- Private pilots may be reimbursed for aircraft operating expenses directly related to search and rescue operations, provided the expenses are rental fees, fuel/oil, airport expenditures.
- If a private pilot is a salesman, he/she may demonstrate a plane for a prospective buyer is he/she has more than 200 hours.
- A private pilot who meets the requirements of 14 CFR §61.69 may act as PIC of an aircraft towing a glider/un-powered trike ultra-light.
- Private pilot cannot be SIC on aircraft carrying passengers or property for compensation or hire
- Can use BasicMed
Medical Certificates: Class, Expiration, Privileges
- And temporary disqualifications, and operations under BasicMed.
- 14 CFR §61.23
Classes of Medical Certificate
- First Class
- Required to PIC with an ATP
- Required to be required pilot flightcrew member if 60 years old
- 40 and older: 6 months
- Under 40: 12 months
- Second Class
- Required for commercial PIC privilages
- 12 Months at any age
- Third Class
- Sufficient for the sport, recreational, student, private, and flight instructor ratings
- 40 and older: 24 months
- Under 40: 60 months
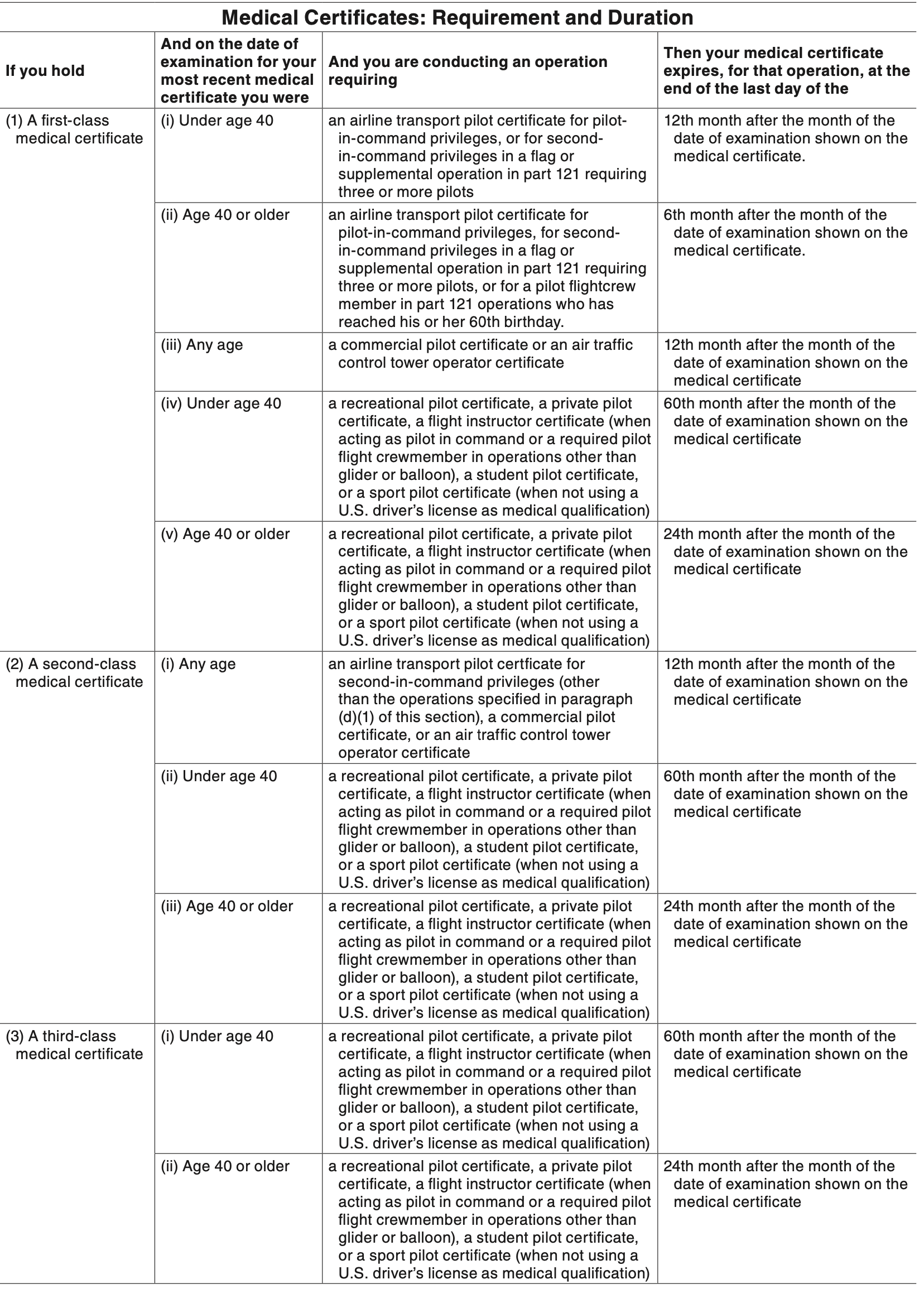
Medical Certificate Details
- 14 CFR §61.23 - Medical certificates: Requirement and duration
- Each of the classes of medical certificates "reverts" to the the lower class at expiration.
BasicMed
- Limitations
- 14 CFR §61.113(i)
- For Private Pilot only
- Airplane authorized to carry not more than 7 people or with max takeoff weight not more than 12,500 lb
- Carry no more than 6 passengers
- Fly no higher than 18,000 ft
- Fly no faster than 250 KIAS
- Cannot fly for compensation or hire
- These limitations were updated in November 2024
- Requirements
- 14 CFR §61.23(c)(3)
- Have held a medical at some point after 14-July-2006
- The most recent medical cannot have been suspended or revoked
- Completed medical education course in previous 24 calendar months
- Received physical exam in previous 48 calendar months
- Bring BasicMed checklist to any licensed physician
- Comply with any medical requirements or restrictions associated with their U.S. driver's license
- FAA-AC-68-1A BasicMed
- FAA Updates BasicMed Program
- FAA BasicMed
Medical Deficiencies
- 14 CFR §61.53 Prohibition on operations during medical deficiency
- If you have a medical certificate and are taking medication or have a condition which would make you no longer meet the requirements then you cannot fly
- Don't fly if you are unable to operate the aircraft in a safe manner
- Certain medical conditions are disqualifying
- Certain medical conditions will result in being issued a medical certificate with a limitation on it
- For example if an applicant fails to meet the color vision standard as interpreted above but is otherwise qualified, the Examiner must issue a medical certificate bearing the limitation
- Not valid for night flying or by color signal control
- Guide for Aviation Medical Examiners Application Process for Medical Certification
- Guide for Aviation Medical Examiners Aerospace Medical Dispositions Item 52. Color Vision
- Another example of a limitation is for someone who is hearing impaired they would require the limitation "not valid for flight requiring the use of radio."
- Some disabilities may require special equipment to be installed in the aircraft, such as hand controls for pilots with paraplegia.
- For example if an applicant fails to meet the color vision standard as interpreted above but is otherwise qualified, the Examiner must issue a medical certificate bearing the limitation
- Statement of Demonstrated Ability (SODA)
- A statement authorizing medical certification of, at the discretion of the Federal Air Surgeon, applicants whose disqualifying condition is static or non-progressive.
- May be issued Letter of Evidence (LOE) that needs to be carried along with medical
- May involve different levels of tests (e.g. Operational Color Vision Test (OCVT), Medical Flight Test (MFT))
- If you have any concern about potential medical deficiency, good idea to get medical certificate in the early stages of flight training
- Remember, medical (and student pilot) certificate is required to solo
- No age limit to log dual received, so potentially could be paying for and receiving a lot of flight training before even being eligible to solo, only to later find out you can't get medical (or it has limitation)

Basic Currency Requirements
- 14 CFR §61.56 - Flight Review
- 14 CFR §61.57 - Recent flight experience: Pilot in command
- To act as PIC
- Flight review within previous 24 calendar months
- 1 hour flight and 1 hour ground training
- Review of Part 91
- Demonstrate safe exercise of pilot certificate
- 1 hour flight and 1 hour ground training
- Checkride counts as flight review
- Flight review within previous 24 calendar months
- To carry persons
- 3 takeoffs/landings within the preceding 90 days
- Same category, class, and type
- Full stop if in tailwheel
- 3 takeoffs/landings within the preceding 90 days
- To carry persons at night (1 hour after sunset and ending 1 hour before sunrise)
- 3 takeoffs/landings within the preceding 90 days
- Same category, class, and type
- Full stop
- 3 takeoffs/landings within the preceding 90 days
- See Kortokrax 2006 which was later rescinded and the Federal Register here.
- Basically, with this change, a non-current pilot can act as PIC with an instructor on board, only for the purposes of regaining currency.
- The update that brought the change from passengers to persons also brought a change to the definition of passenger to clarify that persons providing or receiving flight training are not passengers.
Documents Pilots Must Possess
- A pilot is required to have on them or readily accessible in the plane (PPM):
- P - Pilot certificate
- P - Photo ID
- M - Medical certificate
- As instructor and not acting as PIC, just need
- Instructor certificate
- Pilot certificate
- Instructor certificate it says not valid unless pilot certificate is also carried
- Don't need SFRA course completion certificate, but need to produce it within reasonable time if asked
- 14 CFR §61.3 - Requirement for certificates, ratings, and authorizations
- Student pilots are required to carry their logbook on solo cross-country flights